
Recenzja Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED: Niedrogi, cichszy i trwalszy dzięki technologii Lunar Lake
Intel Lunar Lake czy AMD Zen 5?
Oprócz modelu AMD, Asus wprowadza teraz również kompaktowy Vivobook S 14 OLED z najnowszym procesorem Intel Lunar Lake. W recenzji skupiamy się na wydajności i zachowaniu wentylatorów obu modeli, ponieważ inne komponenty, w tym panel FHD OLED 60 Hz, są wspólne dla obu wariantów.Andreas Osthoff, 👁 Andreas Osthoff (tłumaczenie DeepL / Ninh Duy) Opublikowany 🇺🇸 🇩🇪 ...
Werdykt: Vivobook S 14 to lepszy pakiet z Lunar Lake
Kompaktowy Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED korzysta z opcji Intel Lunar Lake w niektórych obszarach. Chociaż wydajność wielordzeniowa znacznie spada w porównaniu do wariantu AMD, ogólna wydajność jest nadal całkowicie wystarczająca do większości codziennych zadań.
Dużą zaletą są niższe limity mocy, co jest szczególnie zauważalne dzięki znacznie cichszym wentylatorom, które stają się głośne tylko wtedy, gdy CPU i GPU są pod maksymalnym obciążeniem. W przeciwnym razie model Intela pozostaje niezmiennie cichszy niż jego odpowiednik AMD.
Wraz z aktualizacją Lunar Lake, Vivobook S 14 OLED Intel przynosi również dodatkowe funkcje, takie jak Thunderbolt 4, rozszerzone funkcje AI od Microsoftu (Copilot+) i nowoczesny moduł Wi-Fi 7.
Portów jest pod dostatkiem, urządzenia wejściowe są wygodne, a czasy pracy na baterii zostały po raz kolejny poprawione. Osiągając 17 godzin w teście Wi-Fi przy jasności 150 nitów i nieco poniżej 11 godzin przy pełnej jasności, kompaktowy Vivobook S 14 OLED radzi sobie znakomicie, choć jest to również zaleta niskiej rozdzielczości ekranu.
To prowadzi nas do punktu krytyki Vivobooka, ponieważ podstawowa wersja wykorzystuje panel OLED o rozdzielczości 1,920 x 1,200. Obraz jest subiektywnie bardzo dobry i żywy, dostępne są również dokładne profile kolorów.
Panel jest jednak również bardzo refleksyjny (brak ekranu dotykowego), a częstotliwość odświeżania jest ograniczona do zaledwie 60 Hz. Występuje również migotanie PWM, ale przynajmniej Asus oferuje rozwiązanie programowe, aby złagodzić ten problem.
Kolejnym punktem krytyki jest brak rozszerzalnej pamięci RAM, ale jest to wina Intela, ponieważ pamięć RAM jest zintegrowana bezpośrednio z pakietem Lunar Lake.
Z ceną detaliczną wynoszącą 1099 euro lub 1000 dolarów, nowy Vivobook S 14 OLED w wersji Intel jest jednak przekonujący. Jest nie tylko o 300 euro tańszy od wariantu AMD, ale także oferuje lepszy ogólny pakiet jako przenośny codzienny towarzysz dzięki niższej emisji.
Za
Przeciw
Cena i dostępność
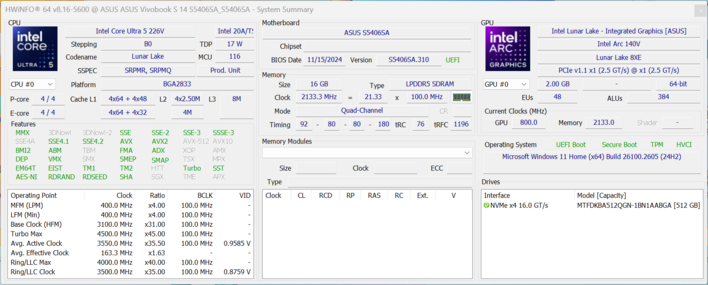
Testowe urządzenie Vivobook S 14 OLED z procesorem Core Ultra 5 226V, 16 GB pamięci RAM i dyskiem SSD o pojemności 512 GB można zamówić bezpośrednio na stronie Asus za 1 099 euro. Model z Core Ultra 7 258V, 32 GB RAM i 1 TB SSD jest obecnie dostępny w Amazon za 999,99 USD.
Porównanie możliwych alternatyw
Obraz | Model / recenzja | Cena | Waga | Wysokość | Ekran |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA Intel Core Ultra 5 226V ⎘ Intel Arc Graphics 130V ⎘ 16 GB Pamięć, 512 GB SSD | Amazon: 1. $949.49 ASUS Vivobook S 14 Copilot+ ... 2. $1,159.00 ASUS Vivobook S 14 Copilot+ ... 3. $899.99 ASUS Vivobook S 14 OLED Slim... Cena katalogowa: 1099€ | 1.3 kg | 15.9 mm | 14.00" 1920x1200 162 PPI OLED | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 ⎘ AMD Radeon 890M ⎘ 24 GB Pamięć, 1024 GB SSD | Amazon: $1,185.21 Cena katalogowa: 1400 EUR | 1.3 kg | 15.9 mm | 14.00" 1920x1200 162 PPI OLED | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU Intel Core Ultra 5 226V ⎘ Intel Arc Graphics 130V ⎘ 16 GB Pamięć, 512 GB SSD | Cena katalogowa: 1200 EUR | 1.3 kg | 16 mm | 14.00" 2880x1800 243 PPI OLED | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 AMD Ryzen 5 7540U ⎘ AMD Radeon 740M ⎘ 16 GB Pamięć, 1024 GB SSD | Amazon: $573.99 Cena katalogowa: 800 EUR | 1.4 kg | 15 mm | 14.00" 1920x1200 162 PPI OLED | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 Intel Core Ultra 7 155H ⎘ Intel Arc 8-Core iGPU ⎘ 32 GB Pamięć, 1024 GB SSD | Amazon: 1. $18.99 Vaxson 2-Pack Protector Film... 2. $12.99 Vaxson 2-Pack Protector Film... 3. $15.99 Vaxson 2-Pack Film Protector... Cena katalogowa: 870€ | 1.4 kg | 15.9 mm | 14.00" 2880x1800 243 PPI IPS | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) AMD Ryzen 7 8845HS ⎘ AMD Radeon 780M ⎘ 32 GB Pamięć, 2048 GB SSD | Amazon: 1. $12.99 Vaxson 2-Pack Protector Film... 2. $15.99 Vaxson 2-Pack Film Protector... 3. $32.99 Vaxson Privacy Screen Protec... Cena katalogowa: 1275€ | 1.4 kg | 18.5 mm | 14.00" 2880x1800 243 PPI IPS | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T Intel Core Ultra 7 155H ⎘ Intel Arc 8-Core iGPU ⎘ 16 GB Pamięć, 1024 GB SSD | Cena katalogowa: 1399€ | 1.3 kg | 17.08 mm | 14.20" 2880x1920 244 PPI OLED |
Testowaliśmy już Vivobook S 14 OLED wyposażony w AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 kilka miesięcy temu. Teraz Asus wprowadza na rynek kolejny model z procesorem Lunar Lake od Intela.
Nasza konfiguracja to model podstawowy za cenę detaliczną 1099 euro, który zapewnia Państwu Core Ultra 5 226V16 GB pamięci RAM, dysk SSD o pojemności 512 GB i panel OLED FHD 60 Hz. Konfiguracja z procesorem Core Ultra 7 258V32 GB pamięci RAM, dyskiem SSD o pojemności 1 TB i panelem OLED 3K 120 Hz wyniesie Państwa 1499 EUR. Dostępność obu wariantów jest obecnie ograniczona.
Specyfikacje
Różnice w stosunku do wariantu AMD
Obudowa Lunar Lake Vivobook S 14 OLED nie różni się od testowanego już modelu już przetestowanego modelu AMD. Wersja Intela jest dostępna w kolorach Black lub Mist Blue, w zależności od opcji procesora.
Jakość wykonania obudowy jest jak najbardziej akceptowalna, a klawiatura oferuje bardzo wygodny skok na poziomie 1,7 mm. Podobnie jak w przypadku modelu AMD, pamięci RAM nie można rozbudować, ponieważ jest ona częścią układu Intela. Dysk SSD M.2 2280 można jednak łatwo wymienić.
Dwa porty USB-C w Intel Vivobook obsługują Thunderbolt 4, a moduł Wi-Fi (Intel BE201) obsługuje również Wi-Fi 7. Jako komputer Copilot+, Vivobook obsługuje teraz zaawansowane funkcje sztucznej inteligencji, takie jak napisy na żywo i efekty Windows Studio dla kamery internetowej 1080p, chociaż sama jakość kamery internetowej pozostaje przeciętna.
Do tej pory wersja AMD również powinna otrzymać niezbędne aktualizacje oprogramowania dla funkcjonalności Copilot+.
| SD Card Reader | |
| average JPG Copy Test (av. of 3 runs) | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (18.4 - 142, n=15, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA (AV PRO microSD 128 GB V60) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) (Angelbird AV Pro V60) | |
| maximum AS SSD Seq Read Test (1GB) | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (22.5 - 207, n=15, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA (AV PRO microSD 128 GB V60) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) (Angelbird AV Pro V60) | |
| Networking | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| iperf3 transmit AXE11000 | |
| iperf3 receive AXE11000 | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| iperf3 transmit AXE11000 | |
| iperf3 receive AXE11000 | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| iperf3 transmit AXE11000 | |
| iperf3 receive AXE11000 | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| iperf3 transmit AXE11000 | |
| iperf3 receive AXE11000 | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| iperf3 transmit AXE11000 | |
| iperf3 receive AXE11000 | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| iperf3 transmit AXE11000 | |
| iperf3 receive AXE11000 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| iperf3 transmit AXE11000 | |
| iperf3 receive AXE11000 | |

Zrównoważony rozwój
Opakowanie składa się głównie z kartonu i materiałów nadających się do recyklingu. Producent nie podaje żadnych dalszych szczegółów na temat wykorzystania materiałów pochodzących z recyklingu w samym urządzeniu ani śladu CO2 podczas produkcji.
Wyświetlacz: Full HD OLED z częstotliwością 60 Hz
Asus postawił również na dobrze znany panel Samsung OLED (ATNA40CT02-0) dla opartego na Intelu Vivobook S 14, który oferuje rozdzielczość 1,920 x 1,200 pikseli w proporcjach 16:10.
Szczegółowe informacje na temat wyświetlacza znajdą Państwo w naszej recenzji wariantu AMDdlatego też skupimy się tutaj tylko na najważniejszych informacjach.
Ekran OLED oferuje wystarczająco ostry obraz o żywych kolorach i wysokim kontraście. Czasy reakcji są szybkie, ale częstotliwość odświeżania OLED jest ograniczona do 60 Hz, co jest zauważalne w codziennym użytkowaniu.
Drugim poważnym problemem jest wysoce odblaskowa powierzchnia, nawet pomimo braku ekranu dotykowego. Jasność SDR wynosi nieco poniżej 400 cd/m², a w trybie HDR osiąga maksymalnie 600 cd/m².
Asus oferuje różne profile kolorów, w tym bardzo dokładne profile dla przestrzeni kolorów Display P3 i sRGB, które są w pełni pokryte.
Występuje migotanie PWM przy 240 Hz, ale Asus oferuje rozwiązanie programowe o nazwie przyciemnianie bez migotania, które pozwala uniknąć klasycznego migotania PWM i pozostać w zakresie przyciemniania DC.
Wydajność: Intel Lunar Lake z LPDDR5x-8533-RAM
Warunki testu
Asus oferuje różne profile wentylatorów, które można również zsynchronizować z profilami energetycznymi systemu Windows. W poniższych testach porównawczych i pomiarach wykorzystaliśmy tryb Performance, który jest połączony z profilem Windows Best Performance.
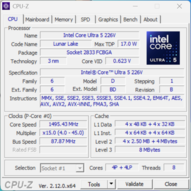
Procesor
Nasze urządzenie testowe jest wyposażone w Intel Core Ultra 5 226V należący do generacji Lunar Lake. Oferuje on cztery szybkie rdzenie wydajnościowe i cztery rdzenie wydajnościowe. Liczba rdzeni jest zatem znacznie niższa niż w przypadku starych procesorów Meteor Lake, a ponieważ skupiono się tutaj bardziej na wydajności, maksymalne TDP jest również znacznie niższe.
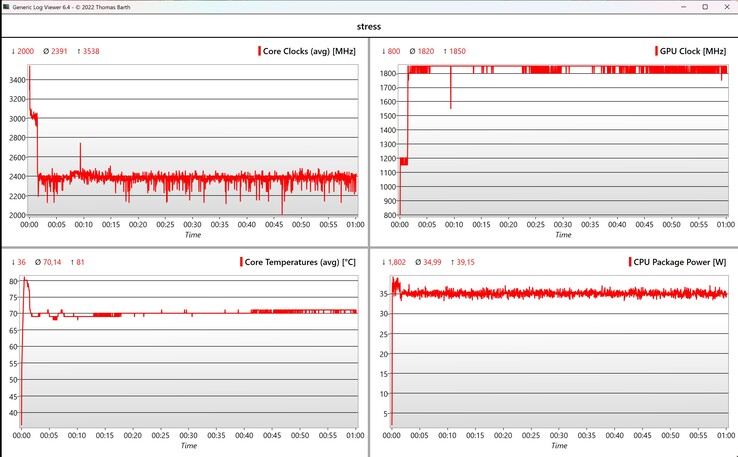
Pod obciążeniem wielordzeniowym procesor początkowo zużywa między 36-39 W, a następnie osiada na stabilnym poziomie 35 W po około 40 sekundach. Wydajność jest zatem ogólnie bardzo stabilna. Jednak wydajność wielordzeniowa nie jest szczególnie dobra, ponieważ konkurenci z układami AMD i starymi procesorami Meteor Lake są znacznie szybsi.
Core Ultra 5 226V wypada lepiej w testach jednordzeniowych, a skumulowana wydajność procesora jest całkowicie wystarczająca do wielu codziennych zastosowań. Jednak procesor AMD Zen 5 z porównywalnie niskimi limitami mocy nadal byłby szybszy w testach wielordzeniowych.
Wydajność pozostaje spójna w trybie bateryjnym. Dalsze testy porównawcze procesora są dostępne tutaj.
Cinebench R15 Multi-core loop
Cinebench R23: Multi Core | Single Core
Cinebench R20: CPU (Multi Core) | CPU (Single Core)
Cinebench R15: CPU Multi 64Bit | CPU Single 64Bit
Blender: v2.79 BMW27 CPU
7-Zip 18.03: 7z b 4 | 7z b 4 -mmt1
Geekbench 6.4: Multi-Core | Single-Core
Geekbench 5.5: Multi-Core | Single-Core
HWBOT x265 Benchmark v2.2: 4k Preset
LibreOffice : 20 Documents To PDF
R Benchmark 2.5: Overall mean
| CPU Performance Rating | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Cinebench R23 / Multi Core | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (1555 - 21812, n=76, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (9827 - 9940, n=4) | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Cinebench R23 / Single Core | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (1699 - 1749, n=4) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (358 - 2165, n=76, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Cinebench R20 / CPU (Multi Core) | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (579 - 8541, n=71, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (3835 - 3885, n=4) | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Cinebench R20 / CPU (Single Core) | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (653 - 674, n=4) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (128 - 826, n=71, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Cinebench R15 / CPU Multi 64Bit | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (327 - 3345, n=77, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (1483 - 1514, n=4) | |
| Cinebench R15 / CPU Single 64Bit | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (261 - 270, n=4) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (72.4 - 322, n=72, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Blender / v2.79 BMW27 CPU | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (159 - 2271, n=75, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (346 - 355, n=4) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| 7-Zip 18.03 / 7z b 4 | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (11668 - 77867, n=67, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (33099 - 33302, n=3) | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| 7-Zip 18.03 / 7z b 4 -mmt1 | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (2643 - 6442, n=69, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (5272 - 5335, n=3) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Geekbench 6.4 / Multi-Core | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (2244 - 17489, n=72, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (9850 - 10151, n=4) | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Geekbench 6.4 / Single-Core | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (2527 - 2584, n=4) | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (960 - 3655, n=67, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Geekbench 5.5 / Multi-Core | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (2557 - 17218, n=68, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (8704 - 8995, n=4) | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Geekbench 5.5 / Single-Core | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (1852 - 1888, n=4) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (726 - 2350, n=68, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| HWBOT x265 Benchmark v2.2 / 4k Preset | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (0.97 - 25.1, n=70, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (12.2 - 12.8, n=4) | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| LibreOffice / 20 Documents To PDF | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (38.5 - 220, n=68, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (45.2 - 61.4, n=4) | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| R Benchmark 2.5 / Overall mean | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (0.403 - 1.456, n=70, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (0.4808 - 0.4873, n=4) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
* ... im mniej tym lepiej
AIDA64: FP32 Ray-Trace | FPU Julia | CPU SHA3 | CPU Queen | FPU SinJulia | FPU Mandel | CPU AES | CPU ZLib | FP64 Ray-Trace | CPU PhotoWorxx
| Performance Rating | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V | |
| AIDA64 / FP32 Ray-Trace | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (1135 - 32888, n=70, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (11849 - 12147, n=4) | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| AIDA64 / FPU Julia | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (59169 - 60179, n=4) | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (5218 - 123315, n=70, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| AIDA64 / CPU SHA3 | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (444 - 5287, n=70, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (2551 - 2570, n=4) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| AIDA64 / CPU Queen | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (10579 - 115682, n=70, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (46991 - 47087, n=4) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| AIDA64 / FPU SinJulia | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (744 - 18418, n=70, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (3909 - 3918, n=4) | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| AIDA64 / FPU Mandel | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (31207 - 32239, n=4) | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (3341 - 65433, n=70, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| AIDA64 / CPU AES | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (638 - 161430, n=70, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (34159 - 36373, n=4) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| AIDA64 / CPU ZLib | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (164.9 - 1379, n=70, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (539 - 572, n=4) | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| AIDA64 / FP64 Ray-Trace | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (610 - 17495, n=70, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (6477 - 6673, n=4) | |
| AIDA64 / CPU PhotoWorxx | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (50038 - 50232, n=4) | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (6569 - 64588, n=70, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
Wydajność systemu
W codziennym użytkowaniu Vivobook S 14 OLED jest bardzo responsywnym komputerem i nie było żadnych problemów ze stabilnością systemu podczas naszych testów. Wyniki benchmarków często plasują się w dolnej średniej; Intel Vivobook wypada jednak lepiej w testach przeglądarek.
CrossMark: Overall | Productivity | Creativity | Responsiveness
WebXPRT 3: Overall
WebXPRT 4: Overall
Mozilla Kraken 1.1: Total
| PCMark 10 / Score | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V, Intel Arc Graphics 130V (6445 - 6734, n=4) | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (4993 - 7788, n=59, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| PCMark 10 / Essentials | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (9363 - 11331, n=59, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V, Intel Arc Graphics 130V (9363 - 10067, n=4) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| PCMark 10 / Productivity | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V, Intel Arc Graphics 130V (8457 - 8977, n=4) | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (5435 - 10623, n=59, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| PCMark 10 / Digital Content Creation | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V, Intel Arc Graphics 130V (8983 - 9239, n=4) | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (5305 - 12442, n=59, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| CrossMark / Overall | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (365 - 2018, n=68, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V, Intel Arc Graphics 130V (1555 - 1582, n=3) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| CrossMark / Productivity | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V, Intel Arc Graphics 130V (1517 - 1539, n=3) | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (364 - 1875, n=68, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| CrossMark / Creativity | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (372 - 2396, n=68, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V, Intel Arc Graphics 130V (1720 - 1740, n=3) | |
| CrossMark / Responsiveness | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (312 - 1899, n=68, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V, Intel Arc Graphics 130V (1225 - 1289, n=3) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| WebXPRT 3 / Overall | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (156 - 479, n=67, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V, Intel Arc Graphics 130V (272 - 286, n=3) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| WebXPRT 4 / Overall | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (132 - 348, n=68, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V, Intel Arc Graphics 130V (249 - 266, n=6) | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Mozilla Kraken 1.1 / Total | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V, Intel Arc Graphics 130V (507 - 543, n=5) | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (278 - 1104, n=76, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
* ... im mniej tym lepiej
| PCMark 10 Score | 6480 pkt. | |
Pomoc | ||
| AIDA64 / Memory Copy | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (99512 - 100584, n=4) | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (14554 - 109035, n=70, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| AIDA64 / Memory Read | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (83885 - 84864, n=4) | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (15948 - 122210, n=70, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| AIDA64 / Memory Write | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (106434 - 111517, n=4) | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (15709 - 117898, n=70, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| AIDA64 / Memory Latency | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (7.2 - 187.8, n=69, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Przeciętny Intel Core Ultra 5 226V (91.1 - 95.6, n=4) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
* ... im mniej tym lepiej
Opóźnienie DPC
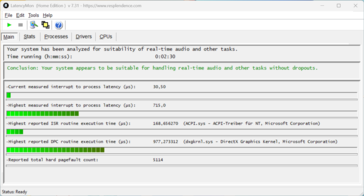
W naszym standardowym teście opóźnień (surfowanie po Internecie, odtwarzanie YouTube w 4K, obciążenie procesora za pomocą Prime95), urządzenie testowe z aktualną wersją BIOS-u nie wykazuje żadnych ograniczeń podczas korzystania z aplikacji audio w czasie rzeczywistym.
| DPC Latencies / LatencyMon - interrupt to process latency (max), Web, Youtube, Prime95 | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
* ... im mniej tym lepiej
Urządzenia pamięci masowej
W naszym urządzeniu zainstalowano dysk SSD Micron 2500 512 GB, przy czym po pierwszym uruchomieniu użytkownik ma do dyspozycji 423 GB. Prędkości transferu dysku SSD M.2 2280 PCIe 4.0 są ogólnie przyzwoite i nie będzie tutaj żadnych problemów.
Wydajność dysku pozostaje również stała nawet przy długotrwałym obciążeniu. Więcej testów porównawczych dysków SSD można znaleźć tutaj.
* ... im mniej tym lepiej
Disk throttling: DiskSpd Read Loop, Queue Depth 8
Karta graficzna
Core Ultra 5 226V jest wyposażony w zintegrowaną jednostkę graficzną Arc Graphics 130V której siedem rdzeni Xe2 osiąga maksymalne taktowanie 1,85 GHz. Przy pełnym obciążeniu GPU zużywa 15 W, a w benchmarkach iGPU musi przyznać się do porażki zarówno z szybszą 8-rdzeniową wersją starego Arc Graphics, jak i z AMD Radeon 780M/890M GPU.
Arc Graphics 130V jest w zupełności wystarczający do codziennych zastosowań multimedialnych, a odtwarzanie filmów w wysokiej rozdzielczości nie stanowi żadnego problemu, ale rezerwy wydajności są ograniczone w przypadku gier.
Mając to na uwadze, w starsze lub mniej wymagające tytuły można zazwyczaj grać płynnie z wysokimi detalami. Wydajność GPU pozostaje na stałym poziomie zarówno przy długotrwałym obciążeniu, jak i w trybie bateryjnym. Więcej testów porównawczych GPU znajdą Państwo w naszej sekcji technologicznej dostępne.
| 3DMark 11 Performance | 8815 pkt. | |
| 3DMark Fire Strike Score | 6913 pkt. | |
| 3DMark Time Spy Score | 3451 pkt. | |
| 3DMark Steel Nomad Light Score | 2413 pkt. | |
Pomoc | ||
| Blender / v3.3 Classroom CPU | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Przeciętny Intel Arc Graphics 130V (550 - 624, n=4) | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (241 - 1127, n=72, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Blender / v3.3 Classroom oneAPI/Intel | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (210 - 368, n=7, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
* ... im mniej tym lepiej
| Cyberpunk 2077 2.2 Phantom Liberty - 1920x1080 Ultra Preset (FSR off) | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (8.48 - 31.4, n=47, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
| GTA V - 1920x1080 Highest Settings possible AA:4xMSAA + FX AF:16x | |
| Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA | |
| SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) | |
| Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA | |
| Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 | |
| Średnia w klasie Subnotebook (7.81 - 53, n=67, ostatnie 2 lata) | |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 | |
Cyberpunk 2077 1080p Ultra FPS chart
| low | med. | high | ultra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTA V (2015) | 151.5 | 131.1 | 60.2 | 20.8 |
| Dota 2 Reborn (2015) | 91.2 | 84.1 | 75.8 | 78.1 |
| Final Fantasy XV Benchmark (2018) | 73.4 | 40.8 | 27.9 | |
| X-Plane 11.11 (2018) | 44.5 | 36.7 | 32.8 | |
| Strange Brigade (2018) | 192.6 | 73.6 | 60.3 | 51.8 |
| Baldur's Gate 3 (2023) | 29.9 | 23.9 | 20.8 | 20.4 |
| Cyberpunk 2077 2.2 Phantom Liberty (2023) | 41.2 | 31.9 | 28.6 | 24.9 |
Emisje i energia: Przewaga Lunar Lake nad Zen 5
Emisja hałasu
Niższe limity mocy Core Ultra 5 226V mają pozytywny wpływ na hałas wentylatora. Przy 45 dB(A), maksymalna wartość w teście obciążeniowym jest wyższa niż w modelu AMD, ale została ona zmierzona również w trybie Standard (odpowiada profilowi Windows Balanced), a w trybie Performance byłaby jeszcze głośniejsza i wynosiłaby poniżej 50 dB(A).
Co więcej, był to maksymalny SPL, jaki mogliśmy zmierzyć w teście obciążeniowym przy pełnym obciążeniu CPU i GPU. W normalnym trybie pracy wariant Intel Vivobook S 14 OLED pozostaje jednak zauważalnie cichszy, a wentylatory również potrzebują czasu, aby zacząć się rozkręcać.
Jest to bardzo zauważalne w praktyce, co sprawia, że Vivobook S 14 OLED jest stosunkowo cichszym urządzeniem. Aktywność wentylatora można jeszcze bardziej zmniejszyć dzięki niższym trybom wentylatora. W naszym urządzeniu testowym nie było żadnych innych odgłosów elektronicznych.
| Tryb wentylatora | Cichy | Standardowy | Moc | Pełna moc |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| maks. głośność wentylatora | 28,8 dB(A) | 42 dB(A) | 45,6 dB(A) | 45,6 dB(A) |
Hałas
| luz |
| 24.2 / 24.2 / 24.2 dB |
| obciążenie |
| 28.8 / 45.6 dB |
 | ||
30 dB cichy 40 dB(A) słyszalny 50 dB(A) irytujący |
||
min: | ||
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA Arc 130V, Core Ultra 5 226V, Micron 2500 MTFDKBA512QGN | Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA Radeon 890M, Ryzen AI 9 HX 370, Micron 2400 MTFDKBA1T0QFM | Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU Arc 130V, Core Ultra 5 226V, Micron 2550 512GB | Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 Radeon 740M, R5 7540U, Micron 2450 1TB MTFDKCD1T0TFK | Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 Arc 8-Core, Ultra 7 155H, YMTC PC300-1TB | SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) Radeon 780M, R7 8845HS, Samsung 990 Pro 2 TB MZVL72T0HDLB | Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T Arc 8-Core, Ultra 7 155H, WD PC SN740 SDDPNQD-1T00 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noise | -6% | -10% | -6% | -6% | -9% | -6% | |
| wyłączone / środowisko * | 24.2 | 24 1% | 25 -3% | 24 1% | 23.8 2% | 25.7 -6% | 25.11 -4% |
| Idle Minimum * | 24.2 | 24 1% | 25 -3% | 25 -3% | 23.8 2% | 25.7 -6% | 25.11 -4% |
| Idle Average * | 24.2 | 25 -3% | 26 -7% | 27 -12% | 23.8 2% | 25.7 -6% | 25.11 -4% |
| Idle Maximum * | 24.2 | 27 -12% | 29 -20% | 29 -20% | 27.1 -12% | 25.7 -6% | 27.2 -12% |
| Load Average * | 28.8 | 40 -39% | 40 -39% | 37 -28% | 34.9 -21% | 36.2 -26% | 31.3 -9% |
| Cyberpunk 2077 ultra * | 37.6 | 39 -4% | 40 -6% | 37 2% | 43.7 -16% | 43.6 -16% | |
| Load Maximum * | 45.6 | 40 12% | 41 10% | 38 17% | 43.7 4% | 43.6 4% | 46.61 -2% |
* ... im mniej tym lepiej
Temperatura
Temperatury powierzchni również pozostają niższe niż w modelu AMD i, poza hotspotem w tylnej środkowej części spodu, prawie nie zmierzyliśmy więcej niż 40 °C w żadnym punkcie, nawet przy maksymalnym obciążeniu.
Oznacza to, że urządzenie może być również używane na udach bez żadnych problemów, a powierzchnie prawie nie nagrzewają się podczas codziennych zadań. W teście obciążeniowym z połączonym obciążeniem CPU i GPU, pobór mocy procesora pozostał na stabilnym poziomie 35 W.
(+) Maksymalna temperatura w górnej części wynosi 38.4 °C / 101 F, w porównaniu do średniej 35.9 °C / 97 F , począwszy od 21.4 do 59 °C dla klasy Subnotebook.
(-) Dno nagrzewa się maksymalnie do 49.7 °C / 121 F, w porównaniu do średniej 39.3 °C / 103 F
(+) W stanie bezczynności średnia temperatura górnej części wynosi 24.5 °C / 76 F, w porównaniu ze średnią temperaturą urządzenia wynoszącą 30.8 °C / ### class_avg_f### F.
(±) 3: The average temperature for the upper side is 32.6 °C / 91 F, compared to the average of 30.8 °C / 87 F for the class Subnotebook.
(+) Podpórki pod nadgarstki i touchpad są chłodniejsze niż temperatura skóry i maksymalnie 27.3 °C / 81.1 F i dlatego są chłodne w dotyku.
(±) Średnia temperatura obszaru podparcia dłoni w podobnych urządzeniach wynosiła 28.2 °C / 82.8 F (+0.9 °C / 1.7 F).
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA Intel Core Ultra 5 226V, Intel Arc Graphics 130V | Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370, AMD Radeon 890M | Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU Intel Core Ultra 5 226V, Intel Arc Graphics 130V | Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 AMD Ryzen 5 7540U, AMD Radeon 740M | Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 Intel Core Ultra 7 155H, Intel Arc 8-Core iGPU | SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) AMD Ryzen 7 8845HS, AMD Radeon 780M | Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T Intel Core Ultra 7 155H, Intel Arc 8-Core iGPU | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat | -18% | -3% | -5% | -9% | -7% | -13% | |
| Maximum Upper Side * | 38.4 | 49 -28% | 41 -7% | 39 -2% | 43.7 -14% | 44.6 -16% | 45.2 -18% |
| Maximum Bottom * | 49.7 | 59 -19% | 45 9% | 46 7% | 49.4 1% | 50.9 -2% | 49.2 1% |
| Idle Upper Side * | 25.1 | 28 -12% | 26 -4% | 28 -12% | 27.7 -10% | 26.5 -6% | 29.6 -18% |
| Idle Bottom * | 25.8 | 29 -12% | 28 -9% | 29 -12% | 28.6 -11% | 26.3 -2% | 30.2 -17% |
* ... im mniej tym lepiej
Głośnik
Dźwięk z głośników stereo jest ogólnie dość przyzwoity, a reprodukcja głosów w szczególności korzysta z wyraźnych wysokich tonów.
Brakuje jednak basów, a ogólny dźwięk wydaje się nieco cienki w zależności od stylu muzycznego lub gatunku filmowego.
Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA analiza dźwięku
(+) | głośniki mogą odtwarzać stosunkowo głośno (86.7 dB)
Bas 100 - 315 Hz
(-) | prawie brak basu - średnio 17.3% niższa od mediany
(±) | liniowość basu jest średnia (10.5% delta do poprzedniej częstotliwości)
Średnie 400 - 2000 Hz
(+) | zbalansowane środki średnie - tylko 3.9% od mediany
(+) | średnie są liniowe (3.8% delta do poprzedniej częstotliwości)
Wysokie 2–16 kHz
(+) | zrównoważone maksima - tylko 3.8% od mediany
(+) | wzloty są liniowe (6% delta do poprzedniej częstotliwości)
Ogólnie 100 - 16.000 Hz
(+) | ogólny dźwięk jest liniowy (13% różnicy w stosunku do mediany)
W porównaniu do tej samej klasy
» 19% wszystkich testowanych urządzeń w tej klasie było lepszych, 4% podobnych, 77% gorszych
» Najlepszy miał deltę 5%, średnia wynosiła ###średnia###%, najgorsza wynosiła 53%
W porównaniu do wszystkich testowanych urządzeń
» 11% wszystkich testowanych urządzeń było lepszych, 2% podobnych, 86% gorszych
» Najlepszy miał deltę 4%, średnia wynosiła ###średnia###%, najgorsza wynosiła 134%
Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU analiza dźwięku
(+) | głośniki mogą odtwarzać stosunkowo głośno (84 dB)
Bas 100 - 315 Hz
(-) | prawie brak basu - średnio 21.5% niższa od mediany
(±) | liniowość basu jest średnia (7.5% delta do poprzedniej częstotliwości)
Średnie 400 - 2000 Hz
(±) | wyższe średnie - średnio 8.3% wyższe niż mediana
(±) | liniowość środka jest średnia (7.6% delta do poprzedniej częstotliwości)
Wysokie 2–16 kHz
(+) | zrównoważone maksima - tylko 3.2% od mediany
(+) | wzloty są liniowe (2.9% delta do poprzedniej częstotliwości)
Ogólnie 100 - 16.000 Hz
(±) | liniowość ogólnego dźwięku jest średnia (20.3% różnicy w stosunku do mediany)
W porównaniu do tej samej klasy
» 63% wszystkich testowanych urządzeń w tej klasie było lepszych, 9% podobnych, 28% gorszych
» Najlepszy miał deltę 5%, średnia wynosiła ###średnia###%, najgorsza wynosiła 53%
W porównaniu do wszystkich testowanych urządzeń
» 50% wszystkich testowanych urządzeń było lepszych, 8% podobnych, 42% gorszych
» Najlepszy miał deltę 4%, średnia wynosiła ###średnia###%, najgorsza wynosiła 134%
Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 analiza dźwięku
(±) | głośność głośnika jest średnia, ale dobra (81 dB)
Bas 100 - 315 Hz
(-) | prawie brak basu - średnio 23.4% niższa od mediany
(±) | liniowość basu jest średnia (9.2% delta do poprzedniej częstotliwości)
Średnie 400 - 2000 Hz
(+) | zbalansowane środki średnie - tylko 4.6% od mediany
(+) | średnie są liniowe (5.4% delta do poprzedniej częstotliwości)
Wysokie 2–16 kHz
(+) | zrównoważone maksima - tylko 2.3% od mediany
(+) | wzloty są liniowe (5.7% delta do poprzedniej częstotliwości)
Ogólnie 100 - 16.000 Hz
(±) | liniowość ogólnego dźwięku jest średnia (17.2% różnicy w stosunku do mediany)
W porównaniu do tej samej klasy
» 42% wszystkich testowanych urządzeń w tej klasie było lepszych, 9% podobnych, 49% gorszych
» Najlepszy miał deltę 5%, średnia wynosiła ###średnia###%, najgorsza wynosiła 53%
W porównaniu do wszystkich testowanych urządzeń
» 29% wszystkich testowanych urządzeń było lepszych, 8% podobnych, 63% gorszych
» Najlepszy miał deltę 4%, średnia wynosiła ###średnia###%, najgorsza wynosiła 134%
Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 analiza dźwięku
(+) | głośniki mogą odtwarzać stosunkowo głośno (83.3 dB)
Bas 100 - 315 Hz
(±) | zredukowany bas - średnio 14.4% niższy od mediany
(±) | liniowość basu jest średnia (10.7% delta do poprzedniej częstotliwości)
Średnie 400 - 2000 Hz
(±) | wyższe średnie - średnio 5% wyższe niż mediana
(+) | średnie są liniowe (5.1% delta do poprzedniej częstotliwości)
Wysokie 2–16 kHz
(+) | zrównoważone maksima - tylko 1.9% od mediany
(+) | wzloty są liniowe (5.7% delta do poprzedniej częstotliwości)
Ogólnie 100 - 16.000 Hz
(+) | ogólny dźwięk jest liniowy (12.6% różnicy w stosunku do mediany)
W porównaniu do tej samej klasy
» 17% wszystkich testowanych urządzeń w tej klasie było lepszych, 4% podobnych, 79% gorszych
» Najlepszy miał deltę 5%, średnia wynosiła ###średnia###%, najgorsza wynosiła 53%
W porównaniu do wszystkich testowanych urządzeń
» 10% wszystkich testowanych urządzeń było lepszych, 2% podobnych, 88% gorszych
» Najlepszy miał deltę 4%, średnia wynosiła ###średnia###%, najgorsza wynosiła 134%
SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) analiza dźwięku
(±) | głośność głośnika jest średnia, ale dobra (80.9 dB)
Bas 100 - 315 Hz
(-) | prawie brak basu - średnio 27.9% niższa od mediany
(±) | liniowość basu jest średnia (8% delta do poprzedniej częstotliwości)
Średnie 400 - 2000 Hz
(±) | zmniejszone średnie - średnio 6.2% niższe niż mediana
(±) | liniowość środka jest średnia (7.9% delta do poprzedniej częstotliwości)
Wysokie 2–16 kHz
(+) | zrównoważone maksima - tylko 2.6% od mediany
(+) | wzloty są liniowe (4.1% delta do poprzedniej częstotliwości)
Ogólnie 100 - 16.000 Hz
(±) | liniowość ogólnego dźwięku jest średnia (20.7% różnicy w stosunku do mediany)
W porównaniu do tej samej klasy
» 66% wszystkich testowanych urządzeń w tej klasie było lepszych, 8% podobnych, 27% gorszych
» Najlepszy miał deltę 5%, średnia wynosiła ###średnia###%, najgorsza wynosiła 53%
W porównaniu do wszystkich testowanych urządzeń
» 53% wszystkich testowanych urządzeń było lepszych, 8% podobnych, 39% gorszych
» Najlepszy miał deltę 4%, średnia wynosiła ###średnia###%, najgorsza wynosiła 134%
Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T analiza dźwięku
(+) | głośniki mogą odtwarzać stosunkowo głośno (83.1 dB)
Bas 100 - 315 Hz
(±) | zredukowany bas - średnio 6.4% niższy od mediany
(±) | liniowość basu jest średnia (10.7% delta do poprzedniej częstotliwości)
Średnie 400 - 2000 Hz
(±) | wyższe średnie - średnio 6.1% wyższe niż mediana
(+) | średnie są liniowe (6.5% delta do poprzedniej częstotliwości)
Wysokie 2–16 kHz
(+) | zrównoważone maksima - tylko 1.7% od mediany
(+) | wzloty są liniowe (4.4% delta do poprzedniej częstotliwości)
Ogólnie 100 - 16.000 Hz
(+) | ogólny dźwięk jest liniowy (10.6% różnicy w stosunku do mediany)
W porównaniu do tej samej klasy
» 8% wszystkich testowanych urządzeń w tej klasie było lepszych, 3% podobnych, 89% gorszych
» Najlepszy miał deltę 5%, średnia wynosiła ###średnia###%, najgorsza wynosiła 53%
W porównaniu do wszystkich testowanych urządzeń
» 5% wszystkich testowanych urządzeń było lepszych, 1% podobnych, 94% gorszych
» Najlepszy miał deltę 4%, średnia wynosiła ###średnia###%, najgorsza wynosiła 134%
Zużycie energii
Pomiary zużycia energii wykazują wyraźną przewagę testowanego urządzenia nad jego odpowiednikiem AMD. Fakt, że zużycie energii jest znacznie niższe pod obciążeniem, nie jest zaskakujący ze względu na niższe limity mocy, ale model Lunar Lake ma również przewagę w trybie bezczynności z identycznym wyświetlaczem.
Określamy maksymalny pobór mocy na poziomie 62,7 W, który następnie szybko spada do około 58 W. Ze względu na niższe zużycie, Asus może użyć bardziej kompaktowego zasilacza 65 W (223 g) zamiast adaptera 90 W, który jest również wystarczająco zwymiarowany.
| wyłączony / stan wstrzymania | |
| luz | |
| obciążenie |
|
Legenda:
min: | |
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA Arc 130V, Core Ultra 5 226V, Micron 2500 MTFDKBA512QGN | Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA Radeon 890M, Ryzen AI 9 HX 370, Micron 2400 MTFDKBA1T0QFM | Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU Arc 130V, Core Ultra 5 226V, Micron 2550 512GB | Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 Radeon 740M, R5 7540U, Micron 2450 1TB MTFDKCD1T0TFK | Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 Arc 8-Core, Ultra 7 155H, YMTC PC300-1TB | SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) Radeon 780M, R7 8845HS, Samsung 990 Pro 2 TB MZVL72T0HDLB | Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T Arc 8-Core, Ultra 7 155H, WD PC SN740 SDDPNQD-1T00 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power Consumption | -71% | -15% | -22% | -60% | -65% | -37% | |
| Idle Minimum * | 2.7 | 6 -122% | 5 -85% | 5 -85% | 4.4 -63% | 4.8 -78% | 4.4 -63% |
| Idle Average * | 6.7 | 8 -19% | 6 10% | 6 10% | 9.2 -37% | 8.7 -30% | 5.6 16% |
| Idle Maximum * | 6.9 | 14 -103% | 10 -45% | 10 -45% | 9.6 -39% | 9.2 -33% | 12.5 -81% |
| Load Average * | 34.5 | 76 -120% | 36 -4% | 41 -19% | 62.6 -81% | 63.2 -83% | 52.1 -51% |
| Cyberpunk 2077 ultra * | 43 | 58.6 -36% | 41.6 3% | 42.5 1% | 71.5 -66% | 81.3 -89% | |
| Cyberpunk 2077 ultra external monitor * | 41.9 | 61.9 -48% | 38.2 9% | 71.9 -72% | 80.2 -91% | ||
| Load Maximum * | 62.7 | 94 -50% | 60 4% | 58 7% | 101.7 -62% | 94.5 -51% | 67.3 -7% |
| Witcher 3 ultra * | 46.7 |
* ... im mniej tym lepiej
Power consumption: Cyberpunk 2077 / Stress test
Power consumption: External monitor
Żywotność baterii
Żywotność baterii modelu AMD Vivobook S 14 OLED była już doskonała, ale wariant Lunar Lake działa jeszcze dłużej. W teście WLAN przy jasności 150 cd/m² (co odpowiada 68% maksymalnej jasności SDR w testowanym urządzeniu) zmierzyliśmy 17:10 godzin, a więc o 40 minut dłużej niż w przypadku Zen 5 SKU.
Nawet przy pełnej jasności Vivobook S 14 może wytrzymać 11 godzin. Pętla wideo H.264 1080p działa nawet przez około 20 godzin przy 150 nitach. Są to doskonałe wartości.
| Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA Core Ultra 5 226V, Arc 130V, 75 Wh | Asus VivoBook S 14 OLED M5406WA Ryzen AI 9 HX 370, Radeon 890M, 75 Wh | Acer Swift 14 AI SF14-51-58TU Core Ultra 5 226V, Arc 130V, 65 Wh | Lenovo Yoga Slim 6 14APU8 R5 7540U, Radeon 740M, 60 Wh | Xiaomi RedmiBook Pro 14 2024 Ultra 7 155H, Arc 8-Core, 80 Wh | SCHENKER VIA 14 Pro (M24) R7 8845HS, Radeon 780M, 60 Wh | Huawei MateBook 14 FLMH-W7611T Ultra 7 155H, Arc 8-Core, 70 Wh | Średnia w klasie Subnotebook | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Czasy pracy | -5% | -27% | -43% | -17% | -52% | -8% | -26% | |
| H.264 | 1199 | 1251 4% | 612 -49% | 961 ? -20% | ||||
| WiFi v1.3 | 1030 | 990 -4% | 753 -27% | 590 -43% | 888 -14% | 571 -45% | 758 -26% | 757 ? -27% |
| Load | 174 | 165 -5% | 101 -42% | 64 -63% | 194 11% | 121.3 ? -30% |
Ogólna ocena Notebookcheck
Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED korzysta z niższego zużycia energii przez procesor Intel Lunar Lake i oferuje lepszy ogólny pakiet jako kompaktowy towarzysz, pomimo niższej wydajności wielordzeniowej. Wentylatory są cichsze, temperatury niższe, a czasy pracy na baterii są jeszcze lepsze.
Asus Vivobook S 14 OLED S5406SA
- 29/12/2024 v8
Andreas Osthoff
Przezroczystość
Wyboru urządzeń do recenzji dokonuje nasza redakcja. Próbka testowa została udostępniona autorowi jako pożyczka od producenta lub sprzedawcy detalicznego na potrzeby tej recenzji. Pożyczkodawca nie miał wpływu na tę recenzję, producent nie otrzymał też kopii tej recenzji przed publikacją. Nie było obowiązku publikowania tej recenzji. Nigdy nie przyjmujemy rekompensaty ani płatności w zamian za nasze recenzje. Jako niezależna firma medialna, Notebookcheck nie podlega władzy producentów, sprzedawców detalicznych ani wydawców.
Tak testuje Notebookcheck
Każdego roku Notebookcheck niezależnie sprawdza setki laptopów i smartfonów, stosując standardowe procedury, aby zapewnić porównywalność wszystkich wyników. Od około 20 lat stale rozwijamy nasze metody badawcze, ustanawiając przy tym standardy branżowe. W naszych laboratoriach testowych doświadczeni technicy i redaktorzy korzystają z wysokiej jakości sprzętu pomiarowego. Testy te obejmują wieloetapowy proces walidacji. Nasz kompleksowy system ocen opiera się na setkach uzasadnionych pomiarów i benchmarków, co pozwala zachować obiektywizm.































 Total Sustainability Score:
Total Sustainability Score: 







